TreeSet in Java is an implementation class of SortedSet interface that uses a tree for storage. Java TreeSet is the most important part of the collection framework. TreeSet class in Java came in Java 1.2 version. In Java TreeSet objects are stored in sorted and ascending order, therefore, access and retrieval time are quite fast, which makes TreeSet is the best choice when storing a large amount of sorted information that must be found very quickly.
The important points about TreeSet in Java:
1. The underlying data structure for TreeSet is Tree.
2. Java TreeSet doesn't allow you to store duplicates elements.
3. In Java TreeSet insertion order is not preserved.
4. Java TreeSet doesn't allow you to store heterogeneous objects, it will give you ClassCastException if you are trying to insert heterogeneous elements.
5. If you are depending on default natural sorting order then objects should be homogeneous and comparable. If the objects are not comparable and homogeneous then it will give you a runtime exception.
6. Java TreeSet allows you to insert the null element but only once till Java 6 version.
7. Java TreeSet is the best choice for storing large amounts of sorted information.
Read: What is an exception in Java and how to handle it?
1. TreeSet(): The first constructor creates an empty tree set where elements are sorted in ascending order according to default natural sorting order.
2. TreeSet(Comparator comp): The second constructor creates an empty tree set where elements will be inserted according to the customized sorting order using a comparator object.
3. TreeSet(Collection c): The third constructor creates a tree set that contains the elements of collection c.
4. TreeSet(SortedSet ss): The fourth constructor creates a tree set that contains the elements of SortedSet ss.
2. Object first(): This method returns the first element from TreeSet if TreeSet is not null else it will give you a runtime exception NoSuchElementException.
3. Object last(): This method returns the last element from TreeSet if TreeSet is not null else it will give you a runtime exception NoSuchElementException.
4. boolean contains(Object obj): This method returns true if TrreeSet contains the specified object else it returns false.
5. void clear(): This method is used to remove all the elements from TreeSet.
6. int size(): This method is used to return the size of the set.
7. boolean remove(Object obj): This method is used to remove the specified element from TreeSet.
8. boolean isEmpty(): This method returns true if the set contains no element.
9. Object clone(): This method returns the shallow copy of TreeSet instance.
Read: What are the various methods in the SortedSet interface?
Read: What are the various methods in the NavigableSet interface?
Output:
Output:
The important points about TreeSet in Java:
1. The underlying data structure for TreeSet is Tree.
2. Java TreeSet doesn't allow you to store duplicates elements.
3. In Java TreeSet insertion order is not preserved.
4. Java TreeSet doesn't allow you to store heterogeneous objects, it will give you ClassCastException if you are trying to insert heterogeneous elements.
5. If you are depending on default natural sorting order then objects should be homogeneous and comparable. If the objects are not comparable and homogeneous then it will give you a runtime exception.
6. Java TreeSet allows you to insert the null element but only once till Java 6 version.
7. Java TreeSet is the best choice for storing large amounts of sorted information.
Read: What is an exception in Java and how to handle it?
Constructors in Java TreeSet:
There are 4 constructors are defined in Java TreeSet, which are described below:
1. TreeSet(): The first constructor creates an empty tree set where elements are sorted in ascending order according to default natural sorting order.
2. TreeSet(Comparator comp): The second constructor creates an empty tree set where elements will be inserted according to the customized sorting order using a comparator object.
3. TreeSet(Collection c): The third constructor creates a tree set that contains the elements of collection c.
4. TreeSet(SortedSet ss): The fourth constructor creates a tree set that contains the elements of SortedSet ss.
Methods in Java TreeSet class:
Java TreeSet defines all the methods which are available in NavigableSet, SortedSet, and collection interface. Some of them are discussed below:
1. void add(Object obj): This method is used to add the elements in TreeSet according to some sorting order.
2. Object first(): This method returns the first element from TreeSet if TreeSet is not null else it will give you a runtime exception NoSuchElementException.
3. Object last(): This method returns the last element from TreeSet if TreeSet is not null else it will give you a runtime exception NoSuchElementException.
4. boolean contains(Object obj): This method returns true if TrreeSet contains the specified object else it returns false.
5. void clear(): This method is used to remove all the elements from TreeSet.
6. int size(): This method is used to return the size of the set.
7. boolean remove(Object obj): This method is used to remove the specified element from TreeSet.
8. boolean isEmpty(): This method returns true if the set contains no element.
9. Object clone(): This method returns the shallow copy of TreeSet instance.
Read: What are the various methods in the SortedSet interface?
Read: What are the various methods in the NavigableSet interface?
TreeSet Example in Java:
import java.util.*;
class Person
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
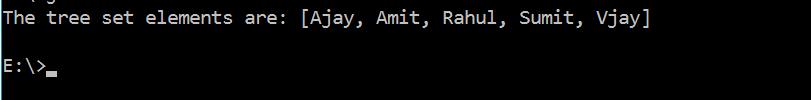
//creating a tree set
TreeSet tset = new TreeSet();
//adding elements in the tree set
tset.add("Ajay");
tset.add("Vijay");
tset.add("Amit");
tset.add("Sumit");
tset.add("Rahul");
//displaying elements
System.out.println("The tree set elements are: " +tset);
}
}Output:
Java TreeSet Example to add a heterogeneous element:
Java TreeSet doesn't allow you to store heterogeneous objects, it will give you ClassCastException if you are trying to insert heterogeneous elements.
import java.util.*;
class Person
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//creating a tree set
TreeSet tset = new TreeSet();
//adding elements in the tree set
tset.add("Ajay");
tset.add("Vijay");
tset.add("Amit");
tset.add("Sumit");
tset.add("Rahul");
//add heterogenos element
tset.add(new Integer(10));
//displaying elements
System.out.println("The tree set elements are: " +tset);
}
}Output:
Java TreeSet example to insert a null element in the non-empty tree set:
If we are trying to insert the null element in non-empty tree set, it will give you a runtime exception because null element compared to the existing elements and null value can't be compared to any element.
import java.util.*;
class treeSetExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//creating a tree set
TreeSet tset = new TreeSet();
//adding elements in the tree set
tset.add("Ajay");
tset.add("Vjay");
tset.add("Amit");
tset.add("Sumit");
tset.add("Rahul");
//add heterogenos element
tset.add(null);
//displaying elements
System.out.println("The tree set elements are: " +tset);
}
}
Note: Insert the new value in the tree set till all 6 versions of Java was allowed but after Java version 6 it was considered a null pointer exception.
Java TreeSet example to insert String Buffer type of elements:
If we are depending on default natural sorting order than the object should be comparable and homogeneous, An object is said to be comparable if its corresponding class implements the Comparable interface. In this example, Ist condition is satisfied nut 2nd condition is not satisfied because StringBuffer class does implement the Comparable interface.
import java.util.*;
class Person
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//creating a tree set
TreeSet tset = new TreeSet();
//adding elements in the tree set
tset.add(new StringBuffer("Ajay"));
tset.add(new StringBuffer("Vjay"));
tset.add(new StringBuffer("Amit"));
tset.add(new StringBuffer("Sumit"));
tset.add(new StringBuffer("Rahul"));
//displaying elements
System.out.println("The tree set elements are: " +tset);
}
}Output:
You may also like these related posts:
How to add and remove elements from ArrayList?
How to implement LinkedList in Java?
HashSet class in Java with Example
LinkedHashSet in Java with Example
JSP Standard Tag Library- JSTL Tutorial
Java MySQL Database Connectivity with Example
Session Management tutorial in Java with Example
TreeSet in Java with Example
 Reviewed by Prashant Srivastava
on
March 08, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Prashant Srivastava
on
March 08, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by Prashant Srivastava
on
March 08, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Prashant Srivastava
on
March 08, 2019
Rating:









No comments: